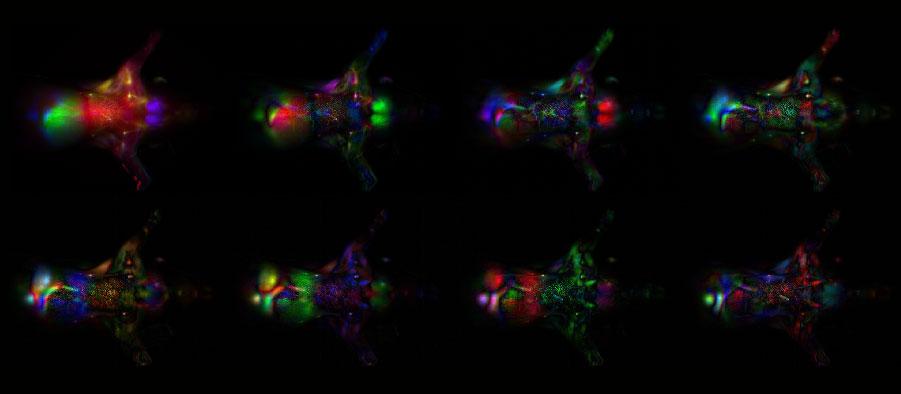About Us | About Nanomedicine | About Deep Tissue Optical Imaging
Nanomedicine & Image-Guided Interventions Laboratory
Research in the Nanomedicine and Image-guided Interventions Laboratory at the Marquette University and Medical College of Wisconsin Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering encompasses multiple research areas including fundamental investigations of near-infrared and shortwave infrared light transport in tissue, development of novel imaging and light-triggered therapeutic nanoparticles, and the integration of optical and multimodal imaging and remotely triggered nanotechnologies into clinical image-guided intervention workflows. The overall objective of these methods is to develop minimally invasive and non-toxic diagnostic and therapeutic technologies directed at cancer, pulmonary and infectious disease, and other vascular pathologies.
Learn more about NIGIL Research
About Nanomedicine
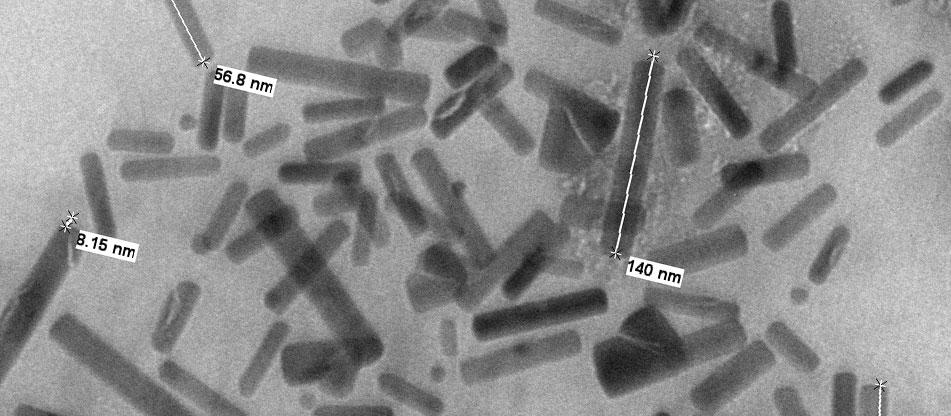
Nanoparticles for biomedical applications are smaller than cells and of the same size as intracellular organelle such as ribosomes. By exploiting the size and surface chemistries of these nanoparticles, we can alter their pharmacokinetics and biodistribution for highly selective imaging and treatment of diseases such as cancer and vascular diseases. To facilitate this process, NIGIL works with biocompatible nanoparticles that can be precisely designed to respond to and leverage light wavelength windows favorable for deep tissue penetration.
Learn more About Nanomedicine
National Cancer Institute | National Nanotechnology Initiative
About Deep Tissue Optical Imaging
Deep tissue optical imaging leverages the multiple-centimeter transport of near-infrared photons in tissue. This transport takes place via multiple scattering, and understanding the resultant distribution of optical energy in tissue and developing image reconstruction algorithms requires advanced mathematical modeling. The Nanomedicine and Image-guided Intervention Laboratory works on both the theoretical and experimental aspects of near-infrared photon migration in tissue and houses multiple wide-area optical image scanners for small and large animal models.
Learn more about NIGIL Facilities
Join Us!
NIGIL seeks to train undergraduate, graduate and postdoctoral scientists in all aspects of translational, optical, and multimodal image-guided interventions while innovating imaging contrasts, methods and systems for precisely targeted treatments of human diseases. For more information on becoming a student in the Nanomedicine and Image-guided Interventions Laboratory, contact Dr. Joshi.