Contact Us!
For more information on the Fan Flow Integrated Research Laboratory, contact Dr. Lei Fan.
Report a Problem
To report a problem with this website, contact BME Communications, or report an accessibility issue.
 Cardiac resynchronization therapy is a commonly used therapeutic option for certain types of heart failure. With this therapy, a 3-lead pacemaker is implanted into the heart to synchronize contractions of the left and right ventricle with each other and the atria. When successful, the therapy improves synchronization of heart-chamber contraction. While the response rate in a given patient is generally positive, the response rate varies widely (between 40 and 95%) depending on which methodology is used to evaluate it. This variance prevents the optimization of lead placement, resulting in suboptimal results for the patient.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy is a commonly used therapeutic option for certain types of heart failure. With this therapy, a 3-lead pacemaker is implanted into the heart to synchronize contractions of the left and right ventricle with each other and the atria. When successful, the therapy improves synchronization of heart-chamber contraction. While the response rate in a given patient is generally positive, the response rate varies widely (between 40 and 95%) depending on which methodology is used to evaluate it. This variance prevents the optimization of lead placement, resulting in suboptimal results for the patient.
The F2IRL seeks to develop an experimentally validated, subject-specific cardiac electromechanics-coronary perfusion computational model to optimize CRT responses to mechanical dyssynchrony with and without ischemia. Findings from this project are translational and are expected to serve as a foundation for future development of patient-specific methodologies to optimize CRT lead locations, improving the responder rate and, ultimately, patient outcome.
F2IRL's research methodology includes using experimental measurements to develop computational models that elucidate activation and deformation patterns at baseline, with mechanical dyssynchrony, and with cardiac resynchronization therapy.
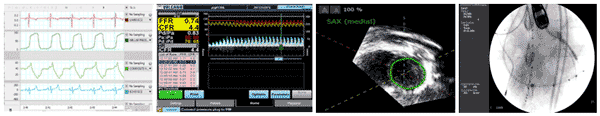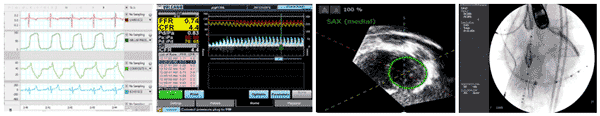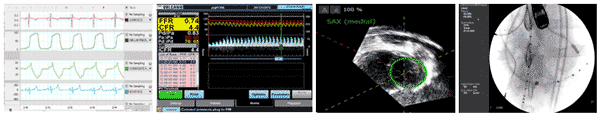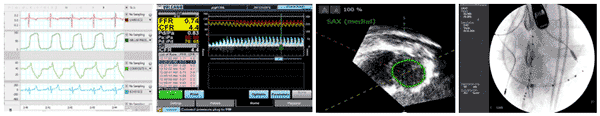 Experimental measurements employed by the F2IRL for CRT response research include (from left to right) left ventricular pressure, volume, and flow rate waveforms; flow velocity mapping; 3D echocardiogram imaging; and angiographic imaging.
Experimental measurements employed by the F2IRL for CRT response research include (from left to right) left ventricular pressure, volume, and flow rate waveforms; flow velocity mapping; 3D echocardiogram imaging; and angiographic imaging.
 Model Development
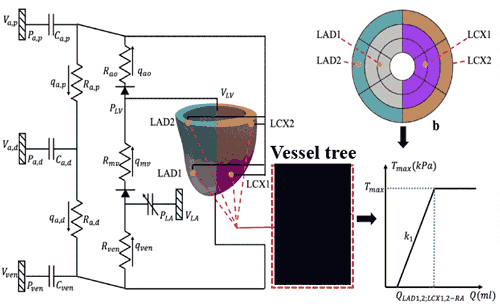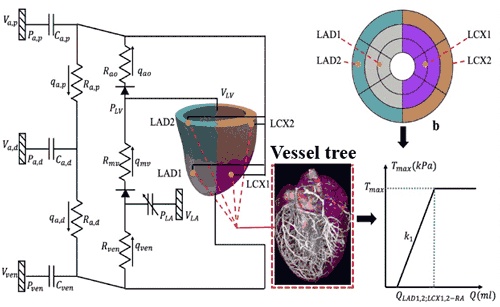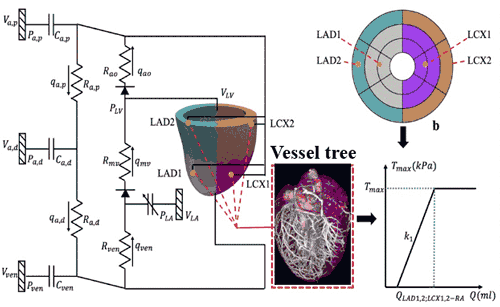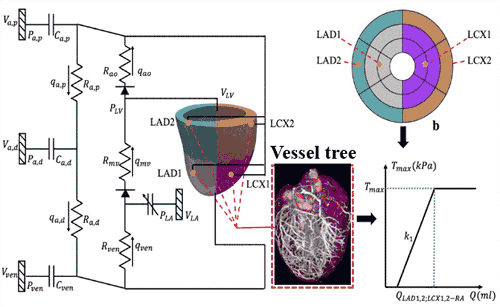
Model DevelopmentIn the Fan Flow Integrated Research Laboratory, models are developed using schematics from intramurally placed ventricular leads.
Data captured from the leads is used to create a vessel tree and determine flow (Q) relative to time (T).
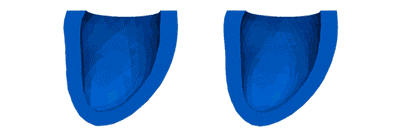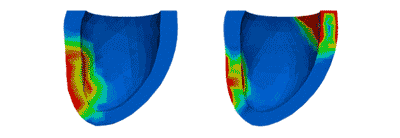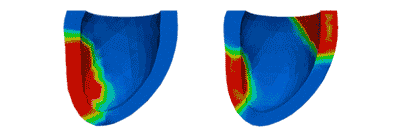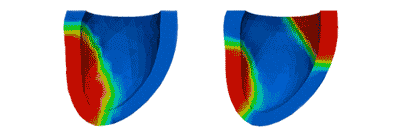 Activation Patterns
Activation PatternsVentricular activation patterns are modeled with mechanical dyssynchrony (left) and with cardiac resynchronization therapy (right).
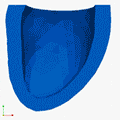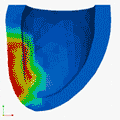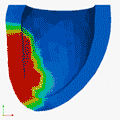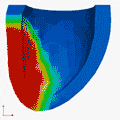
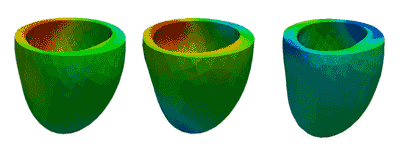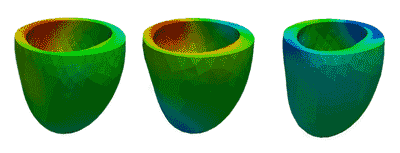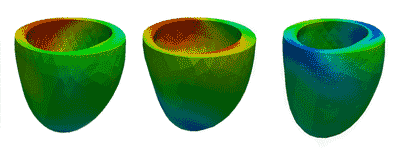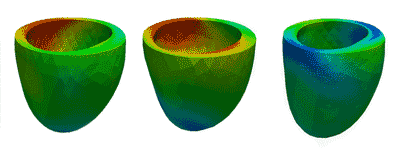 Deformation Patterns
Deformation PatternsVentricular deformation patterns are modeled for the ventricle at baseline (left), with mechanical dyssynchrony (middle) and cardiac resynchronization therapy (right).
Whether seasoned researcher, advanced student or curious undergrad, the Fan Flow Integrated Research Laboratory has opportunities for innovators of all types. For further information on current opportunities to get involved with the F2IRL, contact Principal Investigator Dr. Lei Fan.