Explant Analysis of Spine Arthroplasty Devices, Spine Arthrodesis Devices, and Spine Biomaterials
 A major research theme for OREC's Biomaterials & Histology Laboratory has involved retrieval analysis of explanted spine devices. With the current controversies in large joint arthroplasty, BIMA undertook an analysis of peri-prosthetic tissues from total disc arthroplasty (TDA) explants and found that the particulate debris, corrosion products, and attendant host response found in peri-prosthetic tissues of explanted total disc arthroplasty devices varied with the specific biomaterials used in the device. Therefore, the tissue response associated with one device made of one biomaterial is not the same as the tissue response to a different TDA composed of another biomaterial.
A major research theme for OREC's Biomaterials & Histology Laboratory has involved retrieval analysis of explanted spine devices. With the current controversies in large joint arthroplasty, BIMA undertook an analysis of peri-prosthetic tissues from total disc arthroplasty (TDA) explants and found that the particulate debris, corrosion products, and attendant host response found in peri-prosthetic tissues of explanted total disc arthroplasty devices varied with the specific biomaterials used in the device. Therefore, the tissue response associated with one device made of one biomaterial is not the same as the tissue response to a different TDA composed of another biomaterial.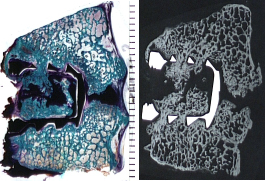
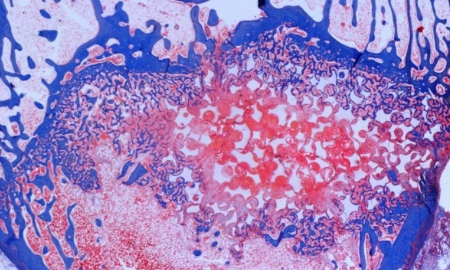
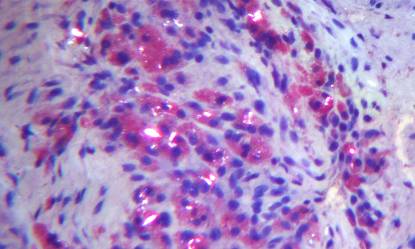
Top: Histology micrograph showing birefringent polymeric debris and Oil Red O stained polymeric debris within macrophages & foreign body giant cells in peri-prosthetic tissues adjacent to an explanted spine device (Oil Red O counterstained with Hematoxylin, partially polarized light, original magnification = 200x). Bottom: Stained undecalcified histology & corresponding microradiograph showing partial bone healing despite a cartilaginous pseudarthrosis within a titanium cervical spinal interbody fusion device (Trichrome Stain, mm scale in field).
Selected Publications
Toth JM, Ankomah F, Kawakami N, Uno K, "A comparison of the inflammatory host response to particulate debris adjacent to unlocked and locked screws of a growth guidance system for early onset scoliosis." European Spine Journal, 31(9), 2301–2310, September 2022.
Toth JM, Bric JD: An Evaluation of the Host Response to an Interspinous Process Device Based on a Series of Spine Explants: Device for Intervertebral Assisted Motion (DIAM®). Journal of Spine Surgery, 5(4): 483-495, 2019.
Kurtz SM, Toth JM, Siskey R, Ciccarelli L, MacDonald D, Isaza J, Lanman T, Punt I, Steinbeck MJ, Goffin J and van Ooij A: The Latest Lessons Learned from Retrieval Analyses of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene, Metal-on-Metal, and Alternative Bearing Total Disc Replacements. Seminars in Spine Surgery, 24(1):57-70, March 2012.
Veruva SY, Steinbeck MJ, Toth JM, Alexander DD, and Kurtz SM: Which Design and Biomaterial Factors Affect Clinical Wear Performance of Total Disc Replacements? A Systematic Review. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 472(12):3759-69, 2014.
Anderson PA, Kurtz S, Toth JM: Explant Analysis of Total Disc Replacement. Seminars in Spine Surgery. 18(2): 109-116, June, 2006.
Anderson PA, Rouleau JP, Toth JM, and Riew KA: A Comparison of Simulator Tested and Retrieved Cervical Disc Prostheses. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine, 1(2):202-210, September 2004.
View more BIMA Research
Join BIMA
The Biomaterials & Histology Laboratory is looking for individuals with an interest in learning more about biomaterials or participating in collaborative research projects. For more information on becoming a member of BIMA, contact Dr. Toth.

 A major research theme for OREC's Biomaterials & Histology Laboratory has involved retrieval analysis of explanted spine devices. With the current controversies in large joint arthroplasty, BIMA undertook an analysis of peri-prosthetic tissues from total disc arthroplasty (TDA) explants and found that the particulate debris, corrosion products, and attendant host response found in peri-prosthetic tissues of explanted total disc arthroplasty devices varied with the specific biomaterials used in the device. Therefore, the tissue response associated with one device made of one biomaterial is not the same as the tissue response to a different TDA composed of another biomaterial.
A major research theme for OREC's Biomaterials & Histology Laboratory has involved retrieval analysis of explanted spine devices. With the current controversies in large joint arthroplasty, BIMA undertook an analysis of peri-prosthetic tissues from total disc arthroplasty (TDA) explants and found that the particulate debris, corrosion products, and attendant host response found in peri-prosthetic tissues of explanted total disc arthroplasty devices varied with the specific biomaterials used in the device. Therefore, the tissue response associated with one device made of one biomaterial is not the same as the tissue response to a different TDA composed of another biomaterial.