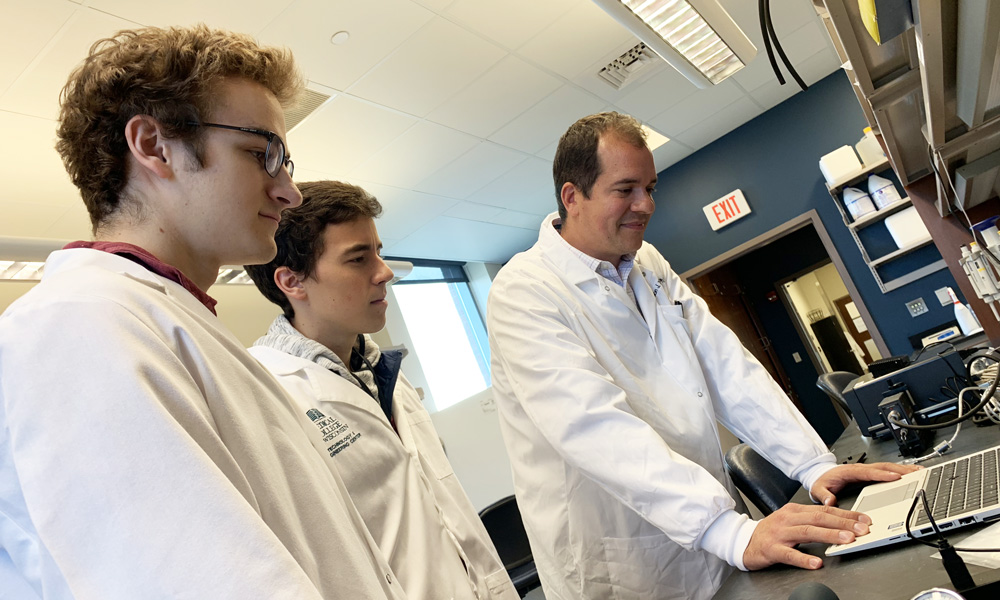
The Cardiovascular Regenerative Engineering Laboratory has facilities located on campuses of both Marquette University and the Medical College of Wisconsin. These facilities are equipped with a variety of resources intended to support investigators in the creation and assessment of engineered tissue constructs.
Featured Capabilities
Expand all | Collapse all
Chemical Synthesis Station
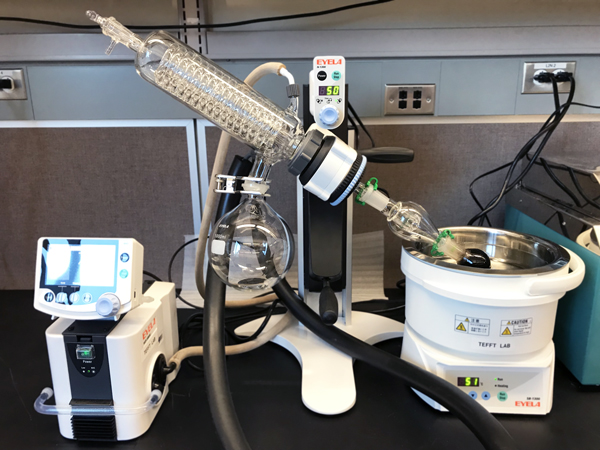 The Chemical Synthesis Station is used to synthesize nanoparticles—including superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION)—for magnetic cell targeting applications.
The Chemical Synthesis Station is used to synthesize nanoparticles—including superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION)—for magnetic cell targeting applications.
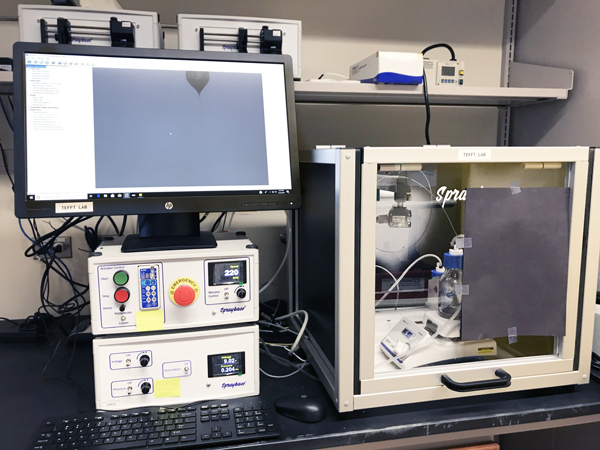 The Electrospinning Station is used to fabricate polymer biomaterials from sub-micron and nanoscale fibers. These biomaterials are useful in cardiovascular regenerative engineering applications.
The Electrospinning Station is used to fabricate polymer biomaterials from sub-micron and nanoscale fibers. These biomaterials are useful in cardiovascular regenerative engineering applications.
Heart Valve Hydrodynamic Performance Test Station
 The Heart Valve Hydrodynamic Performance Test Station is used to assess the hydrodynamic performance of prototype heart valves to ISO 5840 standards. It is capable of applying physiological flows and pressures and measuring effective orifice area and regurgitant fraction.
The Heart Valve Hydrodynamic Performance Test Station is used to assess the hydrodynamic performance of prototype heart valves to ISO 5840 standards. It is capable of applying physiological flows and pressures and measuring effective orifice area and regurgitant fraction.
Vascular Graft Test Station
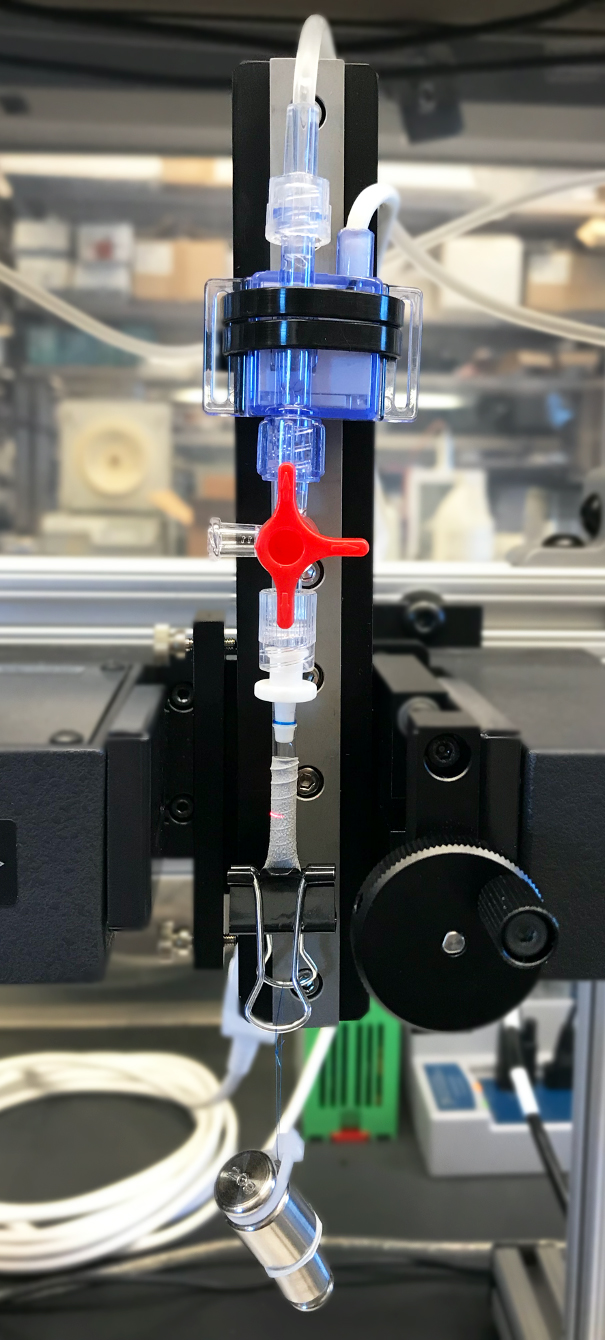 The Vascular Graft Test Station is used to assess the mechanical properties of prototype vascular grafts to ISO 7198 standards. It is capable of applying physiological and super-physiological pressures and measuring dynamic radial compliance and burst strength.
The Vascular Graft Test Station is used to assess the mechanical properties of prototype vascular grafts to ISO 7198 standards. It is capable of applying physiological and super-physiological pressures and measuring dynamic radial compliance and burst strength.
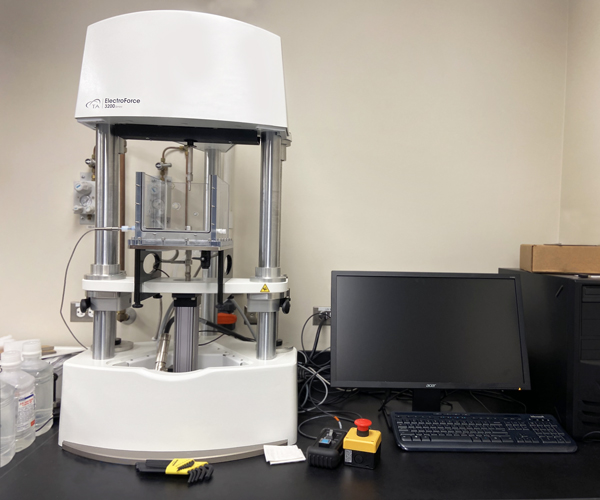 The Mechanical Test Station is used to assess the mechanical properties of biomaterials and tissues. It is capable of dynamic mechanical analysis, tensile testing, and compressive testing.
The Mechanical Test Station is used to assess the mechanical properties of biomaterials and tissues. It is capable of dynamic mechanical analysis, tensile testing, and compressive testing.
Parallel Plate Flow Chambers
 Parallel Plate Flow Chambers are used to expose cells to precise values of steady or pulsatile fluid shear stress.
Parallel Plate Flow Chambers are used to expose cells to precise values of steady or pulsatile fluid shear stress.
 The Cell Culture Facility is used to culture cells using aseptic technique.
The Cell Culture Facility is used to culture cells using aseptic technique.
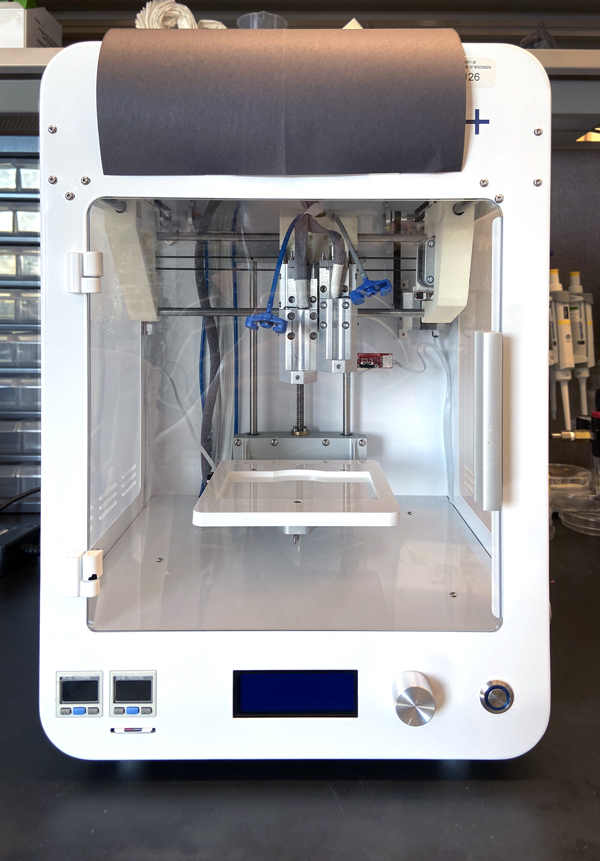 The 3D Bioprinter is used to fabricate three-dimensional constructs consisting of a biomaterial scaffold and one or more cell types in a precise geometric pattern.
The 3D Bioprinter is used to fabricate three-dimensional constructs consisting of a biomaterial scaffold and one or more cell types in a precise geometric pattern.
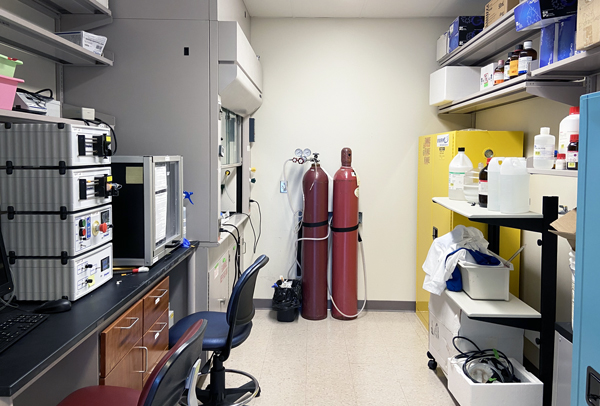 The Chemical Workroom is used to store and handle hazardous chemicals.
The Chemical Workroom is used to store and handle hazardous chemicals.
Fluorescence and Light Microscopy
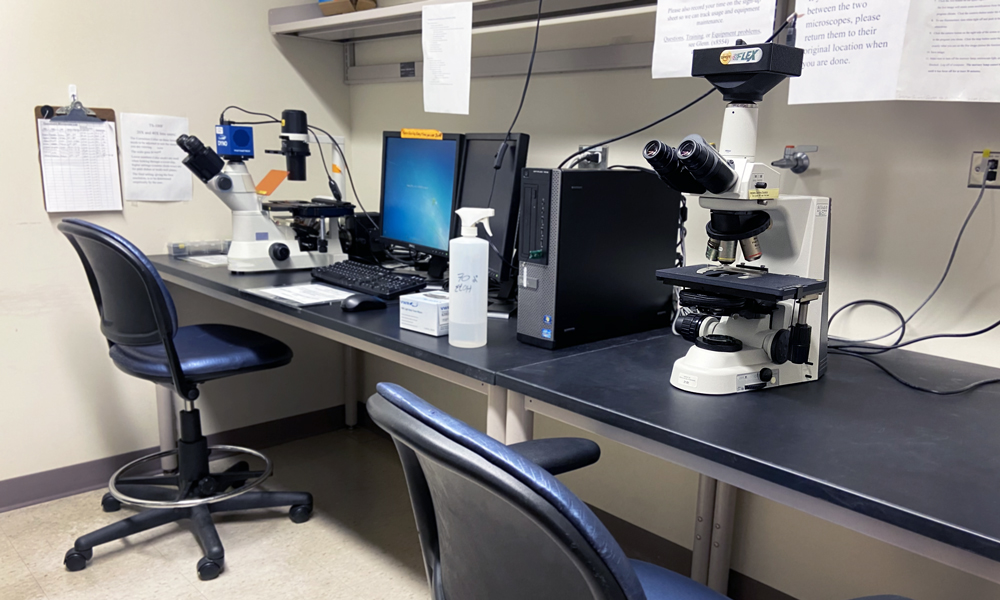 Fluorescence and light microscopy are used to image cells and tissues, typically following a labeling procedure to highlight the structures of interest
Fluorescence and light microscopy are used to image cells and tissues, typically following a labeling procedure to highlight the structures of interest

 The Chemical Synthesis Station is used to synthesize nanoparticles—including superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION)—for magnetic cell targeting applications.
The Chemical Synthesis Station is used to synthesize nanoparticles—including superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION)—for magnetic cell targeting applications. The Electrospinning Station is used to fabricate polymer biomaterials from sub-micron and nanoscale fibers. These biomaterials are useful in cardiovascular regenerative engineering applications.
The Electrospinning Station is used to fabricate polymer biomaterials from sub-micron and nanoscale fibers. These biomaterials are useful in cardiovascular regenerative engineering applications. The Heart Valve Hydrodynamic Performance Test Station is used to assess the hydrodynamic performance of prototype heart valves to ISO 5840 standards. It is capable of applying physiological flows and pressures and measuring effective orifice area and regurgitant fraction.
The Heart Valve Hydrodynamic Performance Test Station is used to assess the hydrodynamic performance of prototype heart valves to ISO 5840 standards. It is capable of applying physiological flows and pressures and measuring effective orifice area and regurgitant fraction. The Vascular Graft Test Station is used to assess the mechanical properties of prototype vascular grafts to ISO 7198 standards. It is capable of applying physiological and super-physiological pressures and measuring dynamic radial compliance and burst strength.
The Vascular Graft Test Station is used to assess the mechanical properties of prototype vascular grafts to ISO 7198 standards. It is capable of applying physiological and super-physiological pressures and measuring dynamic radial compliance and burst strength. The Mechanical Test Station is used to assess the mechanical properties of biomaterials and tissues. It is capable of dynamic mechanical analysis, tensile testing, and compressive testing.
The Mechanical Test Station is used to assess the mechanical properties of biomaterials and tissues. It is capable of dynamic mechanical analysis, tensile testing, and compressive testing. Parallel Plate Flow Chambers are used to expose cells to precise values of steady or pulsatile fluid shear stress.
Parallel Plate Flow Chambers are used to expose cells to precise values of steady or pulsatile fluid shear stress. The Cell Culture Facility is used to culture cells using aseptic technique.
The Cell Culture Facility is used to culture cells using aseptic technique. The 3D Bioprinter is used to fabricate three-dimensional constructs consisting of a biomaterial scaffold and one or more cell types in a precise geometric pattern.
The 3D Bioprinter is used to fabricate three-dimensional constructs consisting of a biomaterial scaffold and one or more cell types in a precise geometric pattern. The Chemical Workroom is used to store and handle hazardous chemicals.
The Chemical Workroom is used to store and handle hazardous chemicals. Fluorescence and light microscopy are used to image cells and tissues, typically following a labeling procedure to highlight the structures of interest
Fluorescence and light microscopy are used to image cells and tissues, typically following a labeling procedure to highlight the structures of interest
