Human Motion Analysis in Cerebral Palsy
Belonging to a group of disorders that negatively impact a person's ability to move and maintain balance and posture, Cerebral Palsy, or CP, is the most common motor disability occurring in childhood, affecting one of every 323 children in the United States. In order to provide appropriate care for affected children, researchers in OREC's Motion Analysis Laboratories have evaluated motion in children and young adults with Cerebral Palsy (CP) for many years. In addition to studies of ambulation and mobility, a substantial effort has been devoted to studies of postural stability. Other work to examine assisted ambulation in children with spastic diplegic CP has revealed similarities in joint kinetics across the glenohumeral, elbow and wrist joints with varying degrees of asymmetry. In another series of studies, descriptive metrics were developed to describe amplitude, regulation, and control of postural sway in children with hemiplegic and diplegic CP. Another set of studies examined kinematic subgroups among youth with hemiplegic CP during locomotion and revealed five distinct subgroups. These findings provide a basis for improved treatment by isolating subgroups with unique characteristics.
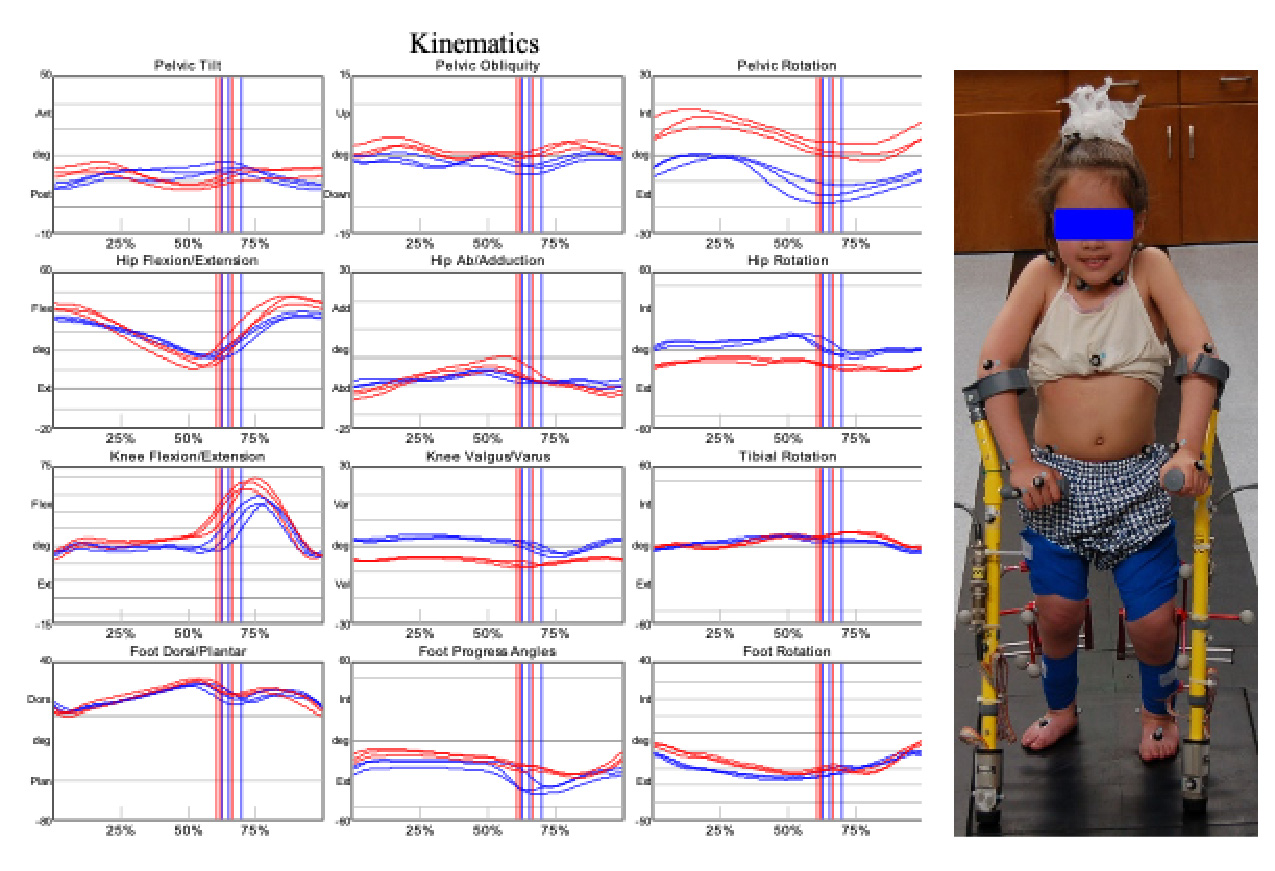
Left Image: Tri-planar Kinematics. Sagittal, Coronal and Transverse Planes in a Population of Control Subjects (grey band) and a Participant with Cerebral Palsy (Red: Right/Blue: Left). Right Image: Participant for Motion Analysis of Upper and Lower Extremities while using Lofstrand Crutches.
Selected Publications
Konop, A., Strifling, K.M., Wang, M., Cao, K., Schwab, J.P., Eastwood, D., Jackson, S., Ackman, J.D. and Harris, G.F.: A Biomechanical Analysis of Upper Extremity Kinetics in Children with Cerebral Palsy using Anterior and Posterior Walkers. Gait and Posture. 30(3):364–369, 2009.
Bustamante Valles, K.D., Long, J.T., Graf, A., Krzak, J., Hassani, S., Riedel, S.A. and Harris, G.F.: Postural Sway in Children with Diplegic and Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy. Critical Reviews in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 23(1–4):95–107,
Krzak, J.J., Corcos, D.M., Graf, A., Smith, P. and Harris, G.F.: Effect of Fine Wire Electrode Insertion on Gait Patterns in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy. Gait and Posture. 37(2):251–257,
Bustamante Valles, , Udoekwere, U., Long, J., Schneider, J., Riedel, S., and Harris, G.F.: A Bidirectional Model of Postural Sway Using Force Plate Data. Critical Reviews in Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, 42 (6): 451–466, 2014.
Krzak, , Corcos, D., Damiano, D., Graf, A., Hedeker, D., Smith, P., and Harris, G.: Kinematic Foot Types in Youth with Equinovarus Secondary to Hemiplegia. Gait and Posture. 41(2):402-408, 2015.
Kruger, K., Konop, K., Krzak, J., Graf, A., Harris, G.F.: Segmental Kinematic Analysis of Planovalgus Feet During Walking in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Gait and Posture, 54, 277–283, 2017.
View More MAL Research
Get Involved!
Opportunities are available for individuals looking to get involved with OREC or the Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Engineering communities.
View Opportunities